Documentation - Example 2
DOCUMENTATION FOR MATHS::SPECIAL::BESSELL::I::BESSEL I
This example shows more uses of Doxygen, including more equations and how to insert a graph:
Brief Description
Modified Bessel function of the first kind of integer order.
Gives this (one part is grayed out due to there being two functions within this module):
Interface |
|
| #include <codecogs/maths/special/bessel/i.h> | |
| double | Maths::Special::Bessel::besselI(double x, double v) |
| Modified Bessel function of the first kind. |
|
| double | Maths::Special::Bessel::besselI (double x, int v) |
| Modified Bessel function of the first kind of integer order. |
|
Detailed Description
These function return solutions to the Modified Bessel Function of the first kind.
The differential equation
\[ z^2 \frac{d^2y}{dz^2} + z \frac{dy}{dz} - (z^2 + v^2)y = 0 \]
where \e v is a real constant, is called the modified Bessel's equation, with the solution known as the modified Bessel function,
with two fundamental solutions: $ I_v(z)$ and $I_{-v}(z)$, where
\[ I_{v}(z) = \frac{z}{2}^v \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{\left ( \frac{z^2}{4}^k \right )}{k! \Gamma(v+k+1)} \]
where $\Gamma(n)$ is the gamma function.
\image html besselI.gif "The Bessel function at varying orders"
A second solution, which is independent of $ I_{v}(z)$, is known as the modified Bessel function of the second kind \ref besselK.
\References
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ModifiedBesselFunctionoftheFirstKind.html
Gives this:
Detailed Description
These function return solutions to the Modified Bessel Function of the first kind.The differential equation
![\[ z^2 \frac{d^2y}{dz^2} + z \frac{dy}{dz} - (z^2 + v^2)y = 0 \]](form_79.png)
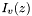 and
and 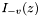 , where
, where
![\[ I_{v}(z) = \frac{z}{2}^v \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{\left ( \frac{z^2}{4}^k \right )}{k! \Gamma(v+k+1)} \]](form_82.png)
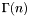 is the gamma function.
is the gamma function.
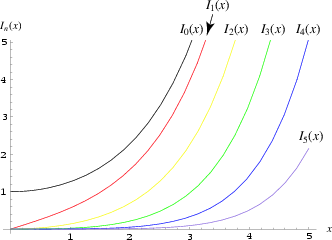
The Bessel function at varying orders
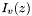 , is known as the modified Bessel function of the second kind besselK.
, is known as the modified Bessel function of the second kind besselK.
The Source Code (+ Function Description)
//! Modified Bessel function of the first kind. /*! Returns modified Bessel function of the first kinds for any order (\a v) The function is defined as \f$ I_1(x) = -i J_1(ix)\f$ The range is partitioned into the two intervals [0,8] and (8, infinity). Chebyshev polynomial expansions are employed in each interval. \param x input argument. \param v order of bessel function. \par Accuracy:Relative error: arithmetic domain # trials peak rms DEC 0, 30 3400 1.2e-16 2.3e-17 IEEE 0, 30 30000 1.9e-15 2.1e-16\Example \code #include#include int main() { using namespace Maths::Special::Bessel; printf("\n x v=0 v=1 v=2 v=3 v=4 v=5"); for(double x=0; x<6; x++) { printf("\nx=%.1lf",x); for(int v=0;v<=5;v++) printf(" %8.6lf", besselI(x,v)); } return 0; } \endcode \Output \code x v=0 v=1 v=2 v=3 v=4 v=5 x=0.0 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 x=1.0 1.266066 0.565159 0.135748 0.022168 0.002737 0.000271 x=2.0 2.279585 1.590637 0.688948 0.212740 0.050729 0.009826 x=3.0 4.880793 3.953370 2.245212 0.959754 0.325705 0.091206 x=4.0 11.301922 9.759465 6.422189 3.337276 1.416276 0.504724 x=5.0 27.239872 24.335642 17.505615 10.331150 5.108235 2.157975 \endcode \author Stephen L. Moshier. Copyright 1984, 1987, 2000 \author Documentation by Will Bateman \References Cephes Math Library Release 2.8: June, 2000 */ double besselI(double x, double v) { ... }
Gives this:
|
||||||||||||
The function is defined as 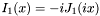
The range is partitioned into the two intervals [0,8] and (8, infinity). Chebyshev polynomial expansions are employed in each interval.
- Parameters:
-
x input argument. v order of bessel function.
- Accuracy:
-
Relative error: arithmetic domain # trials peak rms DEC 0, 30 3400 1.2e-16 2.3e-17 IEEE 0, 30 30000 1.9e-15 2.1e-16
- Example:
-
#include <codecogs/maths/special/bessel/i.h> #include <stdio.h> int main() { using namespace Maths::Special::Bessel; printf("\n x v=0 v=1 v=2 v=3 v=4 v=5"); for(double x=0; x<6; x++) { printf("\nx=%.1lf",x); for(int v=0;v<=5;v++) printf(" %8.6lf", besselI(x,v)); } return 0; }
- Example Output:
-
x v=0 v=1 v=2 v=3 v=4 v=5 x=0.0 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 x=1.0 1.266066 0.565159 0.135748 0.022168 0.002737 0.000271 x=2.0 2.279585 1.590637 0.688948 0.212740 0.050729 0.009826 x=3.0 4.880793 3.953370 2.245212 0.959754 0.325705 0.091206 x=4.0 11.301922 9.759465 6.422189 3.337276 1.416276 0.504724 x=5.0 27.239872 24.335642 17.505615 10.331150 5.108235 2.157975
- Author:
- Stephen L. Moshier. Copyright 1984, 1987, 2000
Documentation by Will Bateman
- References:
- Cephes Math Library Release 2.8: June, 2000
- Source Code:
-
You only own a GNU GPL licence for this module.
You do not own any licences for this module.
