External Mouthpiece
Discharge and Pressure in an External Mouthpiece
Discharge Through An External Mouthpiece
The discharge through an orifice may be increased by fitting a sufficient length of pipe to the outside of the orifice as shown in figure. Such a pipe, which is attached externally to an orifice, is known as an external mouthpiece.
= Height of liquid above the mouthpiece
= Area of the orifice or mouthpiece
= Area of flow at vena contracta
= Coefficient of contraction
= Velocity of liquid at outlet
= Velocity of liquid at vena contracta
It has been experimentally found that there is some loss of head at the entrance of the mouthpiece, depending upon the type of orifice. This loss of head, sometimes, reduces the coefficient of discharge by a small amount (up to 0.82). But, for all practical purposes, the value of coefficient of discharge is taken as 0.855.
The coefficient of discharge for an external mouthpiece also depends upon the length of the pipe. A little consideration will show that the coefficient of discharge will decrease, with the increase in length, due to greater frictional resistance offered by the walls of the mouthpiece to the flowing water.
If the length of the mouthpiece is not given, then the value of coefficient of discharge is taken as 0.855.
Example:
[metric]
Example - Discharge through an external mouthpiece
Problem
Find the discharge from a 100mm diameter external mouthpiece, fitted to one side of a large vessel, if the head over the mouthpiece is 4m.
Workings
Given,
 and discharge through an external mouthpiece,
and discharge through an external mouthpiece,


= 100 mm = 0.1 m
= 4 m
Solution
Pressure In An External Mouthpiece
Consider a vessel, open to the atmosphere at its top, and having an orifice fitted with an external mouthpiece as shown in figure.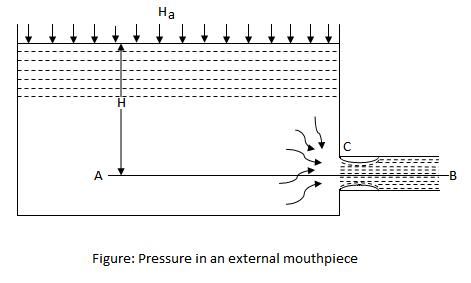
= Atmospheric pressure head
= Height of liquid above the mouthpiece
= Absolute pressure head at vena contracta
= Coefficient of contraction
= Velocity of liquid at outlet
= Velocity of liquid at vena contracta
Example:
[metric]
Example - Pressure in an external mouthpiece
Problem
Water under a constant head of 5 meters is discharging through an external mouthpiece of 100 mm diameter. Determine the absolute pressure head of water at the vena contracta. Take atmospheric pressure as 10.3 m of water.
Workings
Given,

&space;&space;=&space;5.88&space;m)
= 5m
= 100 mm = 0.1m
= 10.3 m
Solution
The absolute pressure head of water = 5.88 m
 Login
Login