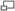The Geometry of Gears
The geometry of both Cycloid and Involute gears. An analysis of the motion between two teeth and the calculation of the path of contact.
Contents
Introduction
It is difficult to imagine machines which do not include some sort of toothed gear system. These are used for the transmission of motion or of power.The systems include Spur gearing in which the axes of the shafts connected are parallel (Note Helical Gearing is the name given to a type of spur gearing in which, although the axes of the shafts are parallel, the teeth are cut on helices instead of straight across the wheel parallel to the axes). Bevel Gearing in which the axes of the shafts intersect and Skew or Spiral Gearing in which the axes are both non parallel and non intersecting.

Velocity Ratio is defined by Classical mechanics as the distance that the point of Effort moved, divided by the distance that the point of Load moved as given from here.
- A constant velocity ratio between the shafts without any possibility of slippage.
- The ability to transmit large torques from the driving to the driven shaft.
Definitions
Before considering the Theory of gear teeth in detail a few necessary definitions are given. These terms are generally used in connection with toothed gearing.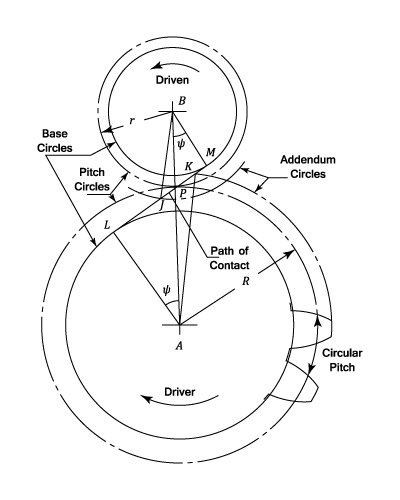
- The Pitch Circle Diameter is the diameter of a circle which by a pure rolling action would transmit the same motion as the actual gear wheel. It should be noted that in the case of wheels which connect non-parallel shafts, the pitch circle diameter is different for each cross section of the wheel normal to the axis of rotation.
- The Pitch Point is the point of contact of two pitch circles.
- The Pitch Line is the line of contact of two Pitch surfaces.
- The Circular Pitch,
is the length of arc round the pitch circle between corresponding points on adjacent teeth.
- The Diametral Pitch,
is the number of teeth per unit length of diameter i.e.
and it can easily be shown that
.
- The Module
- The Path of Contact (
on the diagram) is the path traced out by the point of contact between a pair of teeth. This may be divided into "Approach" and "Recess".
- The Arc of Contact is the arc traced out along the pitch circle whilst one pair of teeth is in contact. Again this can be divided into "Approach" and Recess". It can be shown that the arc of contact
since the path of contact represents a distance round the bases circle.
- The Addendum is the radial length of a tooth from the pitch circle to the tip of the tooth. This is normally constant for a set of gears and the standard value is
- The Dedendum is the radial length of a tooth from the pitch circle to the root of the tooth.
- The Pressure Angle or Angle of Obliquity
is the angle between the common normal
and the tangent at the pitch point
. The normal pressure between teeth acts along
.
- A Pinion is the smaller of two mating gear wheels.
The Motion Transmitted Between Two Teeth
The diagram shows two gear wheels with centers at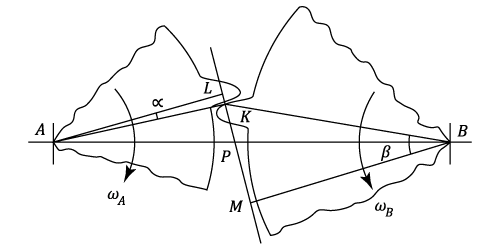
The condition for contact between the teeth to be maintained is that the velocity components along the common normal must be the same for each tooth.
 Or,
Or,
 (by similar triangles)
(by similar triangles)
Thus the condition that there is a constant velocity ratio is that the common normal at the point of contact should pass through a fixed point (The Pitch Point) on the line of centers.
The motion then transmitted is equivalent to the pure rolling of two cylinders with centers at For external gearing,
Cycloid Teeth
A Cycloid is the locus of a point on the circumference of a circle which rolls, without slipping along a straight line.
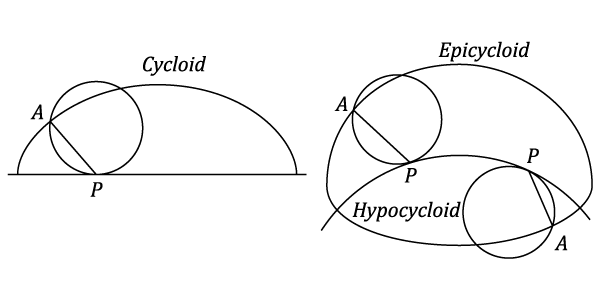
If the circle rolls, without slipping inside or outside a circular arc, the locus of a point on its circumference is termed respectively a Hypocyloid or a Epicycloid.
The three curves are shown in the diagram above.
Gears with cycloidal teeth suffer from the following disadvantages and are little used in modern engineering practice:
- The center distance must be exact in order to achieve a uniform Velocity ratio.
- The Pressure angle, i.e. the direction of the normal teeth between the teeth, varies during the contact of one pair of teeth.
- The teeth on small wheels will be narrower and hence weaker at the root than at the Pitch Line.
Involute Teeth
The outline of a tooth can be traced out by a point on a cord which is unwrapped from a circle (Known as the Base Circle ):- The whole form of the tooth is outside the Base Circle and the common Normal at the point of contact is the common tangent to the Base Circle.
- The path of contact lies along the common tangent.
- The Pressure Angle is constant.
- The center distance for mating gears can be varied, within limits, without upsetting the Velocity Ratio.
- The teeth are thickest at the root which adds strength.

Interference
Interference is the phenomenon in which two waves superpose each other to form a resultant wave of greater or lower amplitude.
The tip of one wheel will undercut the root of a tooth on its mating gear if contact continues outside the common tangent  to the base circles. In a set of gears, this is most likely to occur between teeth of the largest gear wheel, acting against those of the smallest pinion.
The condition for no interference is that
to the base circles. In a set of gears, this is most likely to occur between teeth of the largest gear wheel, acting against those of the smallest pinion.
The condition for no interference is that  .
Interference can be eliminated by a combination of:
.
Interference can be eliminated by a combination of:
- Increasing the angle of obliquity
- Decreasing the addendum of the larger wheel and increasing that of the pinion in such a way as to maintain the same working depth. (i.e. modified teeth)
- Increasing the angle of obliquity and reducing the addenda of all gear wheels (i.e. stub teeth)
- Mating at increased center distances.
Spiral Or Skew Gears
These are used to transmit motion between non-intersecting, non-parallel shafts. The gears must be situated at the shortest distance between the shaft axes and the shaft angle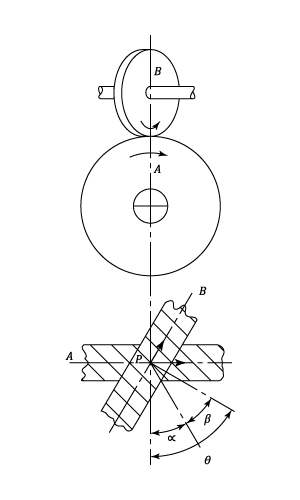
The diagram shows two skew gears
The lower diagram represents the planes of the teeth in contact at the Pitch Point
For teeth of the same hand,
The Normal Circular Pitch
The Normal Diametral Pitch
By analogy with plane involute gears, the Pitch circle diameters are then: and where
The Central Distance
If
Example:
[imperial]
Example - Example 1
Problem
- a) What is the condition that must be satisfied if the velocity ratio between a pair of spur gears is to remain constant during the period of contact between a pair of teeth?
- b) A pair of gears having 40 and 20 teeth respectively, are rotating in mesh with the speed of the smaller being 2000 r.p.m. Determine the speed of sliding between the gear teeth faces at the point of engagement, at the Pitch Point and at the point of disengagement, if the smaller gear is the driver. Assume that the gear teeth are of 20-degree involute form, that the addendum length is 0.200 in. and that the diametral pitch is five.
Workings
- a) See the paragraph on the motion transmitted between two teeth.
- b) From equation (1)
Solution
- The speed at Engagement is
- The speed at Pitch Point is
.
- The speed at Disengagement is
 Login
Login